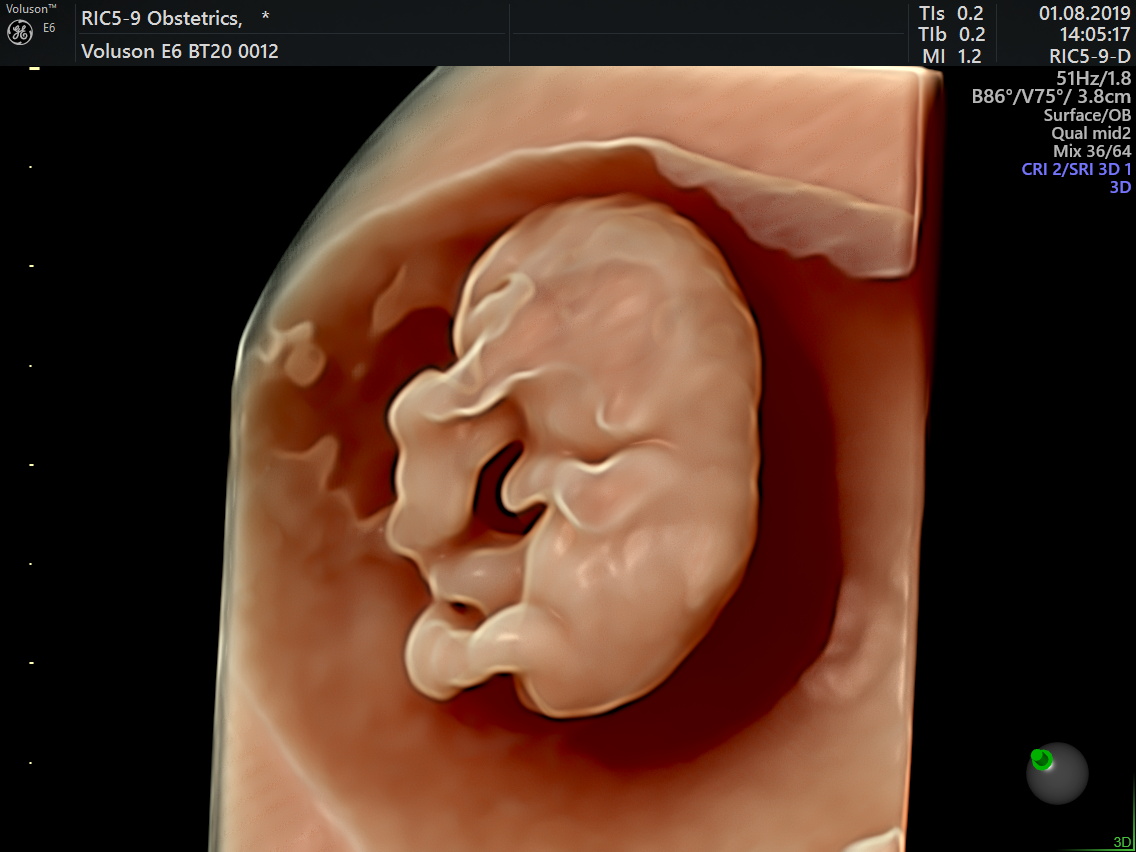
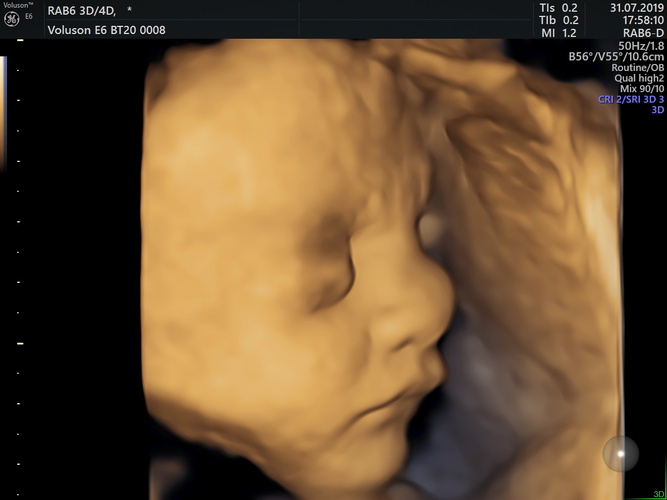
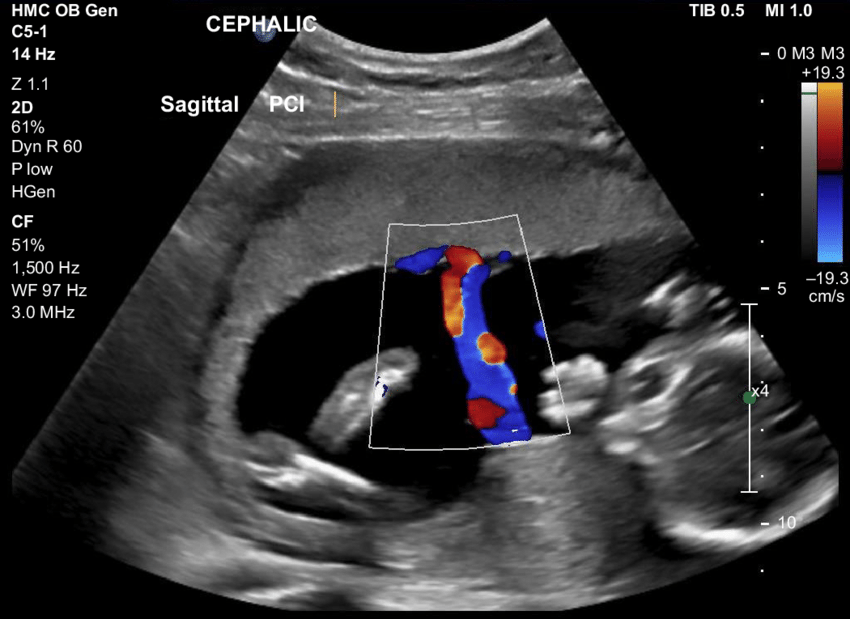
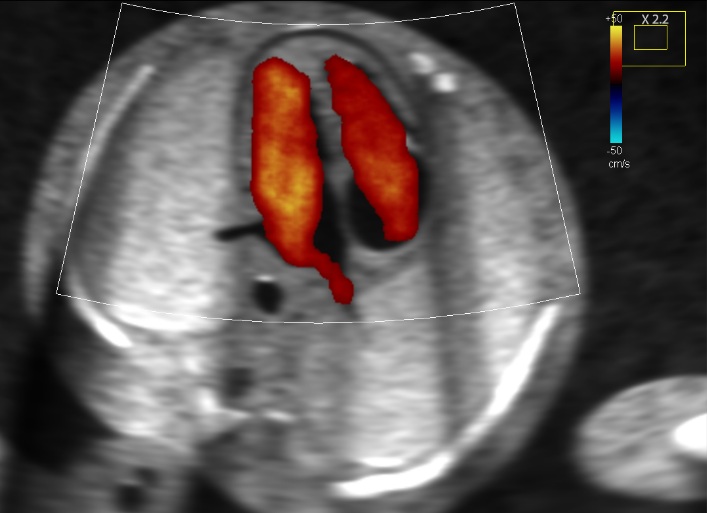
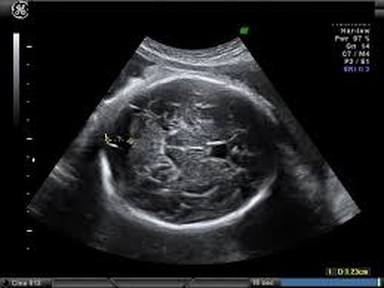
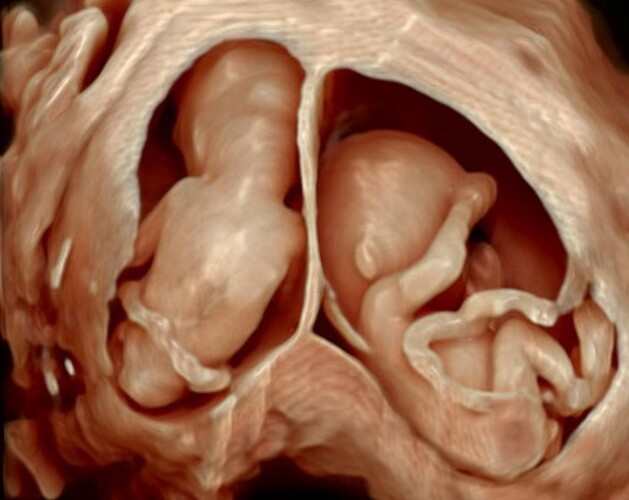
An early pregnancy scan is usually the first ultrasound examination done once the pregnancy is suspected (missed period) and confirmed by a urine pregnancy test (UPT).This scan confirms the presence of pregnancy and its location whether it is inside or outside the uterus.
The number of babies,the chorionicity in case of multiple gestation and the age of pregnancy is determined followed by confirmation of its viability.